Solodex for sale
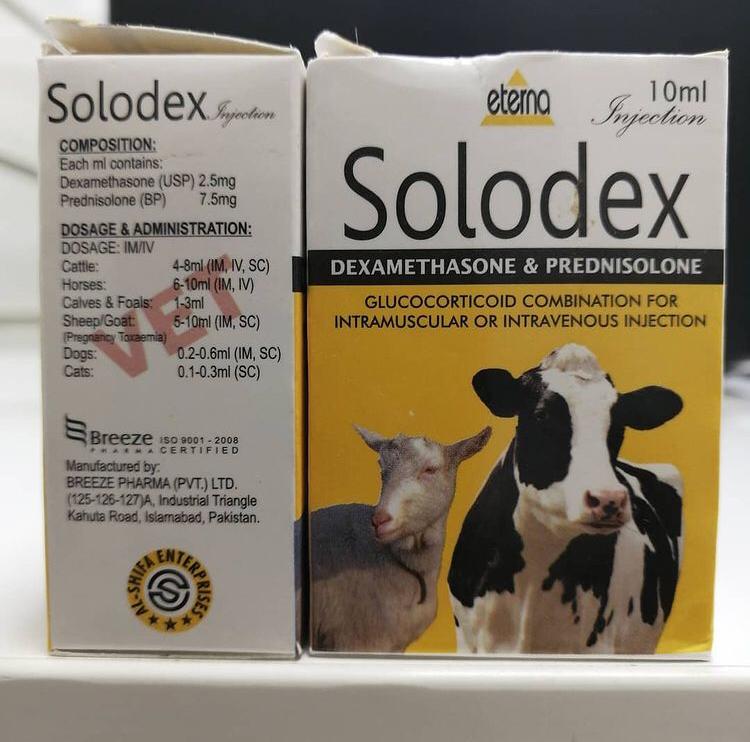
Solodex is a combination medication that relies on the complementary effects of dexamethasone (2.5mg) and prednisolone (7.5mg). Both compounds are glucocorticoids that pump out a potent anti-inflammatory impact coupled with anti-allergic effects. Therefore, the Solodex injection can help with a range of inflammation-related conditions in bovine, ovine, and equine animals, as well as dogs and cats.
Solodex works by dialing back the function of leukocytes, which an animal’s body produces to counteract the danger of an infection or disorder. The medication can be injected to treat ketosis or as part of supportive therapy for:
- Bursitis
- Osteoarthritis
- Tendonitis
- Other musculoskeletal inflammations
- Other conditions that can be improved with glucocorticoids
A Solodex injection 10ml should be given intramuscularly or intravenously. It is not species-specific and can be administered to treat inflammatory conditions in a variety of animals and ages. Some owners also rely on this medication to stimulate weight gain in the animals they care for, but this application has many contraindications. You should seek a professional opinion before injecting Solodex for any purpose.
If you have already consulted a veterinarian, feel free to buy Solodex online at Kihorsemed.com. This glucocorticoid formula can be shipped globally and will include genuine inserts to guide your treatment, injection, and dosage decisions. Our Solodex price is only €45 per 10ml vial.
Is your animal suffering from a severe inflammatory process to a degree where medical condition management can’t wait? Tick the Express Overnight box from your cart to get Solodex in no time.




Reviews
There are no reviews yet.